How does DNS filtering work? DNS filtering and dns filters are designed to combat malware, ransomware, spam attacks, child pornography and other dangerous sites on the web. DNS is both an interpreter and roadmap for the Internet. DNS maps friendly names to IP addresses. Normally, when the browser queries a DNS server, an IP address is returned, allowing the browser to open the website at the specific IP address.
DNS filtering services is the process of using the Domain Name System to block malicious website threats and filter out harmful web content. This ensures that network data remains secure and allows organisations to have control over what their staff can access on company-managed networks.
The DNS server filters the request and blocks it rather than return an IP address. It is also useful for organizations that want to protect internal assets by blocking known malicious sites. This function is normally conducted at the router level by blocking IP addresses or filtering ports. For those without the luxury of high-end routers, DNS filtering and dns filters are a powerful and efficient security solution alternative.
Due to its critical function within both the Internet and the enterprise, DNS is a primary target for hackers so securing it is imperative. An effective dns security strategy entails not only blocking malicious queries but also servicing good queries as well. DNS plays a judicious role in a layered network security strategy in which multiple approaches to cyber defence are required. This multi-tiered approach reduces the possibility of a successful hacking attack.
Sign up for WebTitan DNS Filter FREE trial today.
Book Free Trial
xDNS remains a vulnerable highly targeted component for exploits and cyberattacks. For instance, DNS replies can be spoofed, or created with false information, to redirect users from legitimate sites to malicious websites. Targeting the exploits of cybercriminals however is challenging at best due to the scalability of the Internet. Attackers constantly register new domain names and move to "clean" neighbourhoods. As soon as any security method detects malicious activity and shuts it down, these criminal chameleons simply move to a new location that remains undetected for a while before the cycle repeats itself.
Datto are one of our great friends and partners who use WebTitan DNS content filtering in their routers including the D200 and DNA boxes

DNS filtering should be an important component of your network security strategy used in conjunction with port monitoring, intrusion detection systems, intrusion prevention systems, antivirus, and firewalls. Together, these necessary security layers work cohesively to create a functional and effective security protection system.
DNS Filtering is not without its critics however who point out some of its inherit disadvantages:
For more information about DNS filtering myths visit this recent blog post: 4 Myths about DNS Filtering and some truths
No system is of course bulletproof, and while it is true that cybercriminals are constantly changing domain names, solutions such as WebTitan DNS Filter are highly effective in countering their cloaking efforts. WebTitan dns filter does this by categorizing an estimated 60,000-malware and spyware domains per day, tracking down dangerous sites and blocking them.
A schematic illustrating this process is shown below :
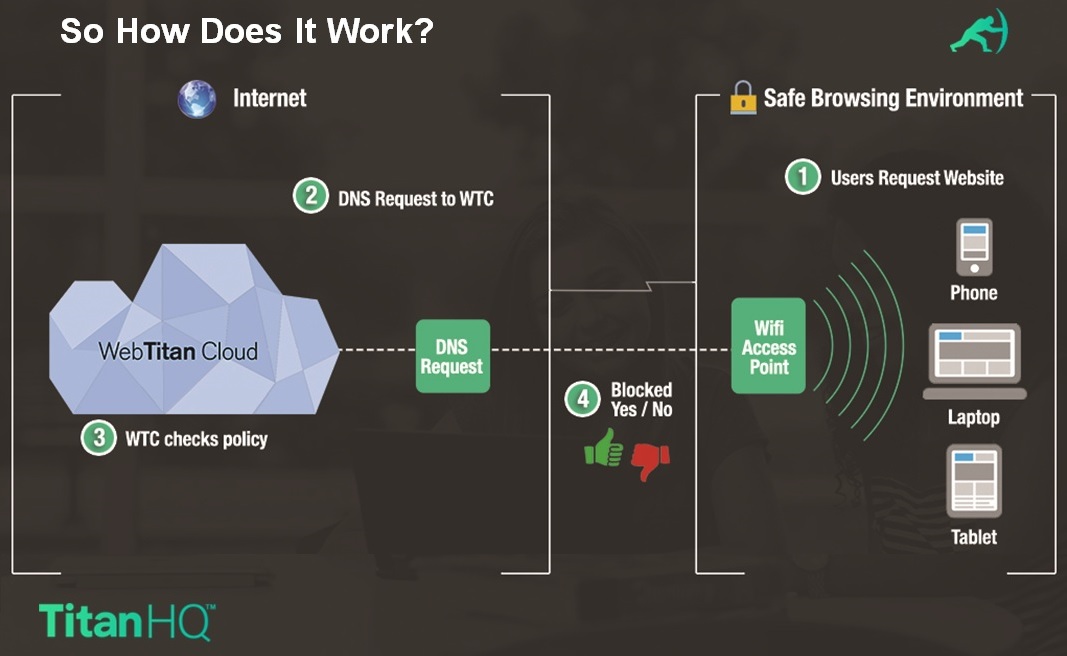
The Domain Name System (DNS) was designed to make it convenient for the public to use the Internet. As mentioned earlier, it translates domain names to the matching IP addresses of the hosted devices. DNS allows us to use https://www.google.com instead of http://74.125.224.72/ to initiate a search. In short, it is the Internet's primary directory service.
The DNS system that services the Internet is a distributed system anchored by a collection of root name servers that are dispersed throughout the world. Under the root servers are top-level domains, (.com, .org, .net) followed by second level domains (google, TitanHQ, Microsoft). These domains form DNS zones, which may consist of one or more domains (for example, google.com is a domain). A set of authoritative name servers are assigned to each DNS zone. An authoritative name server can be either a master or a slave server. A master contains the original read/write copies of zone records while a slave maintains only readable copies of the master records that are updated through replication.
DNS servers use TCP port 53 for zone transfers in order to keep slaves synced with the master zone file. Intruders can use this mechanism to download the contents of a name server’s zone file. To prevent this, administrators should block zone transfer requests from any device that is not an authorized slave name server. Port 53 is often used to tunnel unauthorized traffic and suspicious traffic should be scrutinized.
Sign up for WebTitan DNS Filter FREE trial today.
Book Free TrialA reverse DNS lookup or reverse DNS resolution (rDNS) is the querying of the Domain Name System (DNS) to determine the domain name associated with an IP address – the reverse of the standard "forward" DNS lookup of an IP address from a domain name.
This is often useful in determining the legitimacy of an IP. For example, one of the content tests carried out by the SpamTitan spam filter is to match forward and reverse DNS entries, ensuring that the A records, IP and PTR record match accordingly.
The Association of DHCP and DNS
For IPv4, DNS is most often tightly integrated with Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP). A DHCP server automatically provides IP addresses to DHCP enabled clients as well as other information such as the identity of DNS name servers. The security of DNS therefore requires protecting your DHCP infrastructure. Depending on IPv6 network configuration, DHCP may or may not provide DNS information as Router Advertisement (RA) message provides this information instead.
DNS is a double-edged sword largely because of the insecure nature of the DNS infrastructure, making it vulnerable to these types of attacks:
While DDNS serves a legitimate function of allowing address of a domain name to change quickly and host serves on temporary addresses, it is abused by botnet operators and phishers who change address rapidly to avoid detection
This is another way in which cyber criminals can rapidly alter DNS addresses in order to hide malware and phishing delivery sites behind an ever-changing network of compromised hosts acting as proxies.
This technique is referred to as a Smurf attack (named after the DDoS Smurf malware). It is a distributed denial-of-service attack involving large numbers of ICMP packets with the intended victim's spoofed source IP are broadcast to a computer network using an IP broadcast address.
This popular form of DDoS relies on the use of publically accessible open DNS servers to overwhelm a victim system with DNS response traffic. It is also referred to as a "DRDoS Attack" (Distributed Reflection and Amplification Denial of Service).
Sign up for WebTitan DNS Filter FREE trial today.
Book Free TrialA Distributed Denial of Service attack (DDoS) attack is the purposeful overload of a device to make it unavailable to legitimate traffic. A DDoS usually originates from large numbers of bots or zombie PCs that are under the control of one central machine called a botnet. The motivation behind these attacks can be to bring down a business competitor or as a form of ransomware in which the victim must pay up in order to stop the packet onslaught. One of the largest attacks on record was the Spamhaus attack that occurred in March of 2013 that involved over 30,000 DNS resolvers. Traditional security methods are configured to throttle packets from a designated IP address initiating high amounts of traffic. In the case of Spamhaus, the attackers used an enormous number of different IP addresses so throttling efforts were never triggered. You can read more about Spamhaus here.
Preventing a DNS attack
DNS can be configured to mitigate common DNS security issues. According to the Open Resolver Project, “Open resolvers pose a significant threat to the global network infrastructure”. (https://openresolverproject.org) Keep your DNS server from being an open resolver and restrict its ability to respond to DNS requests from just any address on the Internet. Only allow in-house recursive servers to the IP subnets used by your company. (This includes customer ranges as well if you are operating an extranet.) Keep in mind, however, that many (if not most) DNS resolvers across the Internet are open resolvers, either because they have not been secured, or they are meant to be open to the public such as Comodo’s service. To test your IP address for open resolvers, see https://www.thinkbroadband.com/tools/dnscheck.html
Although there is no sure-fire way to preclude a DNS attack, the following measures can minimize the odds:
For any organization that takes network security seriously, the protection of their DNS infrastructure should be a vital part of their enterprise security plan. A little time and effort spent on DNS security can provide immediate and significant security benefits. For more about our dns filtering product click here
What is WebTitan DNS Filtering?
At its core, WebTitan DNS Filtering is a technique that is used to restrict or block access to certain websites or “domains”. In this way—based on implementation—WebTitan DNS Filtering provides protections in an effort to create a safer, more productive working environment on the Internet. WebTitan DNS Filtering also has other uses and can works with protocols such as ftp and smtp, but for the purposes of this article, we’ll focus on its application for web filtering specifically.
In simple terms, every web server, website, etc, has an address—or more accurately, an Internet Protocol (or IP) address. All machines (e.g. websites, servers, and web services) have an assigned IP address, which enables our computers to locate and connect to other remote computers and enables the communication that supports our World Wide Web. The Domain Name System works to make it easier for humans to use the internet and removes the requirement for us to remember all of those number-only IP addresses. Rather, the DNS system translates readable alphanumeric names and words into a corresponding IPv4 or IPv6 address. DNS servers are located all over the world, mapping IP addresses to their respective domain names—like a worldwide telephone directory for websites.
WebTitan DNS Filtering effectively allows for advanced network security configurations at the domain level. If you try to visit a website and the domain is found to be malicious—a WebTitan DNS Filtering solution might block or redirect that request to a safe page, depending on its configuration.
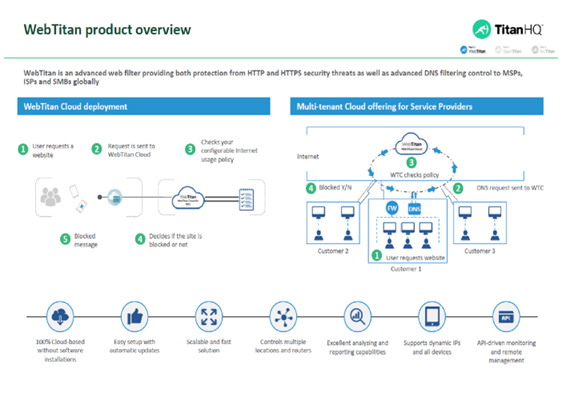
IT departments implemented WebTitan DNS Filtering and configured DNS settings at the router/gateway level on physical machines residing on-premises. In more recent years, businesses have increasingly outsourced these types of administration efforts, relying on external support form Internet Service Providers (ISPs) and Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs). Nowadays, you can purchase a premium or enterprise DNS solution, configure your network to process DNS requests through that service, and be up and running with a functional WebTitan DNS Filtering solution in no time. However, before making a significant decision that has the potential to impact your network security and future cyber protection plans—you should understand the advantages, limitations, and details about scaling a standard ebTitan DNS Filtering solution for web filtering.
WebTitan DNS Filtering is still one of the most important baseline steps towards building a scalable and secure IT infrastructure and can provide advanced protection for everything from pornography to gambling sites, file sharing to news websites, social media, blog platforms, and more.
Sign up for WebTitan DNS Filter FREE trial today.
Book Free TrialThere are a number of critical advantages that a WebTitan DNS Filtering solution provides. But chief among the advantages is the ability to completely block access to malicious and compromised websites, as well as what would be considered “Objectionable” sites such as those hosting content related to pornography, violence, terrorism, and more.
Secondary advantages make WebTitan DNS Filtering an ideal solution for a wide range of businesses and organization. WebTitan DNS Filtering is lightweight, fast, and scalable and with premium and enterprise-level offerings offers advanced flexibility for policy management and customization. Every organization operates differently and has unique requirements and cultural norms as well as web browsing habits. WebTitan DNS Filtering allows IT teams to support custom-tailored configurations with peace of mind.
As mentioned, the most significant advantage WebTitan DNS Filtering gives organizations is the ability to proactively block access to potentially harmful sites, a critical first layer of security and cyber defense. When we look at common payload delivery methods and points of compromise from the various of threats online (i.e. malware, ransomware, phishing attacks, etc.) we find a glaring common denominator. And that is, good old-fashioned user error.
With WebTitan DNS Filtering in place and the proper configuration and support from feeds provided by trusted cybersecurity companies, you able to put up an important wall of defense. When network traffic and users have restricted access to undesirable websites (particularly malicious and objectionable sites) a number of low-hanging security risks are immediately removed.
On top of that, if you’re a business owner, you get the added benefit of preventing those users from accessing the types of materials that could hinder their productivity or cause offense to others throughout the day (i.e. social media, questionable blogging sites, etc.).
Security and filtering providers like WebTitan offer hybrid deployment options that support standard WebTitan DNS Filtering, as well as full-path URL filtering and analysis. This allows an organization to develop and implement advanced solutions that not only support advanced configurations for blocking, redirection, or whitelisting domains, but for full-path content categorization, analysis, malicious detection, traffic analysis, and more. For communications companies, security vendors, and others where security is of primary concern—a scalable and secure infrastructure is critical to scalability, agility, and long-term growth.

The TitanHQ team with one of our DNS filtering partners Fifosys
It's important to remember and understand that no single cybersecurity solution is 100% effective against the evolving threat landscape that we face. WebTitan DNS Filtering goes a long way towards providing you with critical network infrastructure to protect your internet traffic and users—but also requires a robust strategy as well as trusted security cybersecurity partners, feeds, and other technologies to provide maximum protection. Anti-virus, spam filters, two-factor authentication, and remediation policies are also critical to defending your networks.
All in all, WebTitan DNS Filtering allows organizations to enforce comprehensive, forward-thinking and robust Internet usage policies, blocking access to malicious website content and other threats that could potentially do you harm. You might not be able to prevent yourself from becoming the target of a hacker—but with infrastructure and technologies in place like WebTitan DNS Filtering, you can significantly improve your defenses against known threats and reduce the chances of having your network penetrated by accidental user error.
Learn more about how WebTitan DNS filter works and how it can protect your business against malware, phishing, viruses, ransomware and links to malicious websites.
Kick start your WebTitan DNS Filter Free Trial today.
Sign up for WebTitan DNS Filter FREE trial today.
Book Free TrialDNS blocking is used to prevent users from accessing certain websites. DNS blocking is a method of content control. DNS blocking occurs at the DNS lookup stage before any content is downloaded, the process is very quick. The easiest way to block DNS and control the types of content that can be accessed is to use a DNS-based web filter
DNS filtering stands for Domain Name System filtering and is a method of preventing users from accessing certain web pages or IP addresses that may be dangerous or suspicious. When you have a DNS server filter enabled, you can browse the Internet knowing that the DNS filter will prevent you from visiting malicious websites by showing you a “block page” explaining the reason.
DNS filtering is the process of using the Domain Name System to block malicious online threats such as viruses, malware, ransomware, phishing attacks and botnets and filter out harmful or inappropriate content. This ensures that company data remains secure and allows companies to have control over what web content employees can access. WebTitans DNS filtering offers you cloud-based DNS Filtering to bring powerful enterprise filtering to all your users, regardless of their location.
